Healthcare’s New Voice
How AI Text-to-Speech (TTS) technology can improve healthcare
AI text-to-speech (TTS) has stopped being a gimmick and is starting to feel real. It’s like the old obscenity test - “I know it when I hear it.” For most of my life, robotic voices droned through IVR systems, leaving me fully aware that I was talking to a machine. But TTS has hit an inflection point. The most recent AI-generated voices sound so natural they’re practically indistinguishable from human speech. A few years ago, even the best AI voices were clunky and lifeless. Then came profound learning advancements—better speech realism, emotional modulation, and near-instantaneous synthesis. Leading models from ElevenLabs and Cartesia don’t just mimic human voices; they breathe life into them.
I think it's going to be a game-changer for healthcare. Check out these TTS use cases that healthcare companies can implement today. I made these audio samples using the playground features of these AI websites.
Pharmacy prescription pickup
Hi Dan, this is Jamie from Cannon Pharmacy on Main Street. I'm calling to let you know that your prescription for Lisinopril is ready for pickup. We're open until 6 p.m. today. Also, The pharmacist wanted me to let you know that your recent lab work showed that your kidney function is a bit lower than usual, so he adjusted your dosing. He can explain the changes to you when you're here. Thanks, and see you soon!
Insurance claim payment update
Hi Dan, This is Paola from Anthem. I'm calling to update you about claim number 114270, for your Laparoscopic Appendectomy performed by Dr. Ford on 12/27. We discovered that the clinical documents Dr. Ford submitted to us didn't have the proper codes, which has temporarily delayed our claim payment. We're working with the physician to get this fixed but if you have questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out. My extension is 340. Thanks!
Pretty impressive, right? If this was on your voicemail, and you heard it quickly, you might think a real person called you. And that’s pretty different from how these TTS agents felt until recently.
Breakthroughs Driving AI Voice Realism:
Quality and realism are driving this shift. Over the past few years, deep learning breakthroughs have dramatically enhanced the realism and naturalness of TTS, allowing AI voices to approximate human speech patterns closely. These improvements aren't subtle tweaks—they're leaps in fidelity. Synthetic voices can now convey emotion, use natural inflections, and even inject appropriate pauses or laughter.
Massive data sets: Modern text-to-speech models aren’t built on a few hundred hours of data; they’re fueled by millions of hours of high-quality, human-recorded speech across an array of languages and accents. This vast reservoir of sound isn’t just a number—it’s the engine that powers neural networks capable of generalizing across diverse speech patterns, transforming stilted sentences into conversational realism. It’s a leap from limited, echoic samples to an expansive sonic tapestry.
Voice cloning. Imagine replicating a person’s voice with just 5–30 seconds of audio. In the old days, cloning a voice meant laborious data collection and, inevitably, a monotone reproduction. Today, with models like diffusion transformers, every nuance—from the rise and fall of cadence to subtle emotional inflections—is captured. This isn’t merely about replicating sound; it’s about capturing a persona, a unique vocal fingerprint. Suddenly, the synthetic voice becomes a trusted proxy for a real human, and the boundary between machine and man blurs further. Here’s POTUS 47 giving our patient Dan a phone call reminding him about his prescription.
What would it mean for a PCP to use his or her own voice to make routine calls to their panel of patients?
Real-time synthesis: Perhaps the most transformative of all is the reduction in response time. What used to be a few seconds of latency—enough time to remind you that you were talking to a machine—now shrinks to under 100 milliseconds. This dramatic improvement isn’t just an optimization; it redefines our expectations of interactivity. With such efficient inference-time techniques and model compression at work, AI voices now respond almost as naturally as a human conversation partner, ushering in an era where real-time, meaningful interaction is the norm.
It seems that voice AIs have learned the art of bedside manner. As a result, talking to a healthcare AI on the phone or via a smart speaker no longer feels like chatting with a robot; it feels like talking to a helpful human assistant. This has big implications: Patients are more likely to engage with instructions or advice delivered in a comforting, human-like voice than a robotic one.
Who’s Leading the AI Voice Race?
This isn’t an exhaustive list by any means, and certainly not a healthcare-focused one. There are hundreds of players in this space, but I highlighted below five of the more general, industry-agnostic AI TTS platforms. What’s cool is that each of these has a playground that you can mess around with for demos and voice samples, which I used in generating the sample audio files in this blog post.
ElevenLabs: Founded in 2022, ElevenLabs quickly became synonymous with ultra-realistic AI voices. Their voice cloning and expressive reading capabilities have been used in everything from audiobooks to YouTube videos—and now, in healthcare.
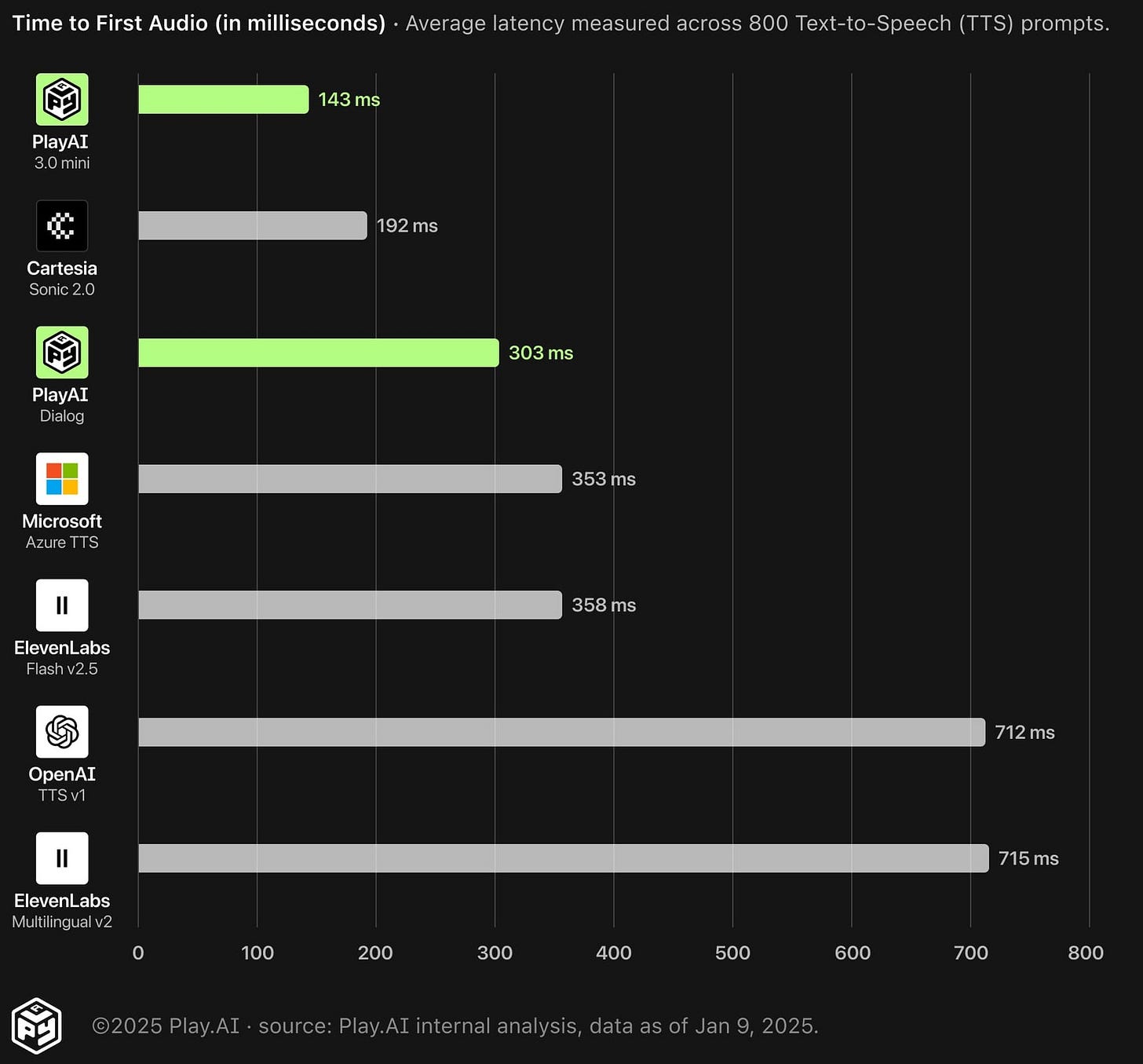
Cartesia (Sonic): Cartesia is making waves with its ultra-low-latency Sonic TTS model, which boasts a time-to-first-audio of just 90 - 200 milliseconds—essentially instant playback. That speed matters. Imagine asking a virtual assistant, “Where’s the nearest urgent care?” and waiting an awkward few seconds for a response—not great in a health emergency. Cartesia’s tech ensures conversations with AI feel fluid and natural. It also supports multilingual output in 13+ languages and can seamlessly switch between accents or languages. This could be a game-changer for hospitals handling diverse patient populations. A single system could speak English to one patient and Spanish to the next without missing a beat. Cartesia also offers fine-grained control over tone and pacing—allowing a softer delivery for palliative care or a more energetic voice for prenatal education.
Zyphra Zonos: In early 2025, Zyphra released Zonos-v0.1, a pair of 1.6-billion-parameter TTS models—including a novel hybrid model—under an Apache 2.0 license. In simple terms, they open-sourced an incredibly powerful voice engine for anyone to use. Zonos models allow high-fidelity voice cloning from just 5–30 seconds of audio and offer precise control over speed, pitch, and even emotions like joy or sadness. Zyphra claims its speech quality "matches or exceeds that of leading proprietary TTS providers"—a bold claim that underscores how far open models have come. For healthcare, this means hospitals and telehealth providers could deploy top-tier voice AI without hefty licensing fees. Imagine a rural clinic running Zonos on its own servers to deliver multilingual voice instructions to patients—dramatically improving accessibility without breaking the bank.
FishSpeech-v1.5: Another open-source standout, FishSpeech v1.5, has been trained on over a million hours of multilingual audio, making it a strong alternative to proprietary TTS services. While its non-commercial license means it's more suited for research or non-profit applications, it demonstrates how rapidly AI voices are being democratized. A hospital IT team or medical research center could experiment with FishSpeech to develop their own voice applications—say, a multilingual voice assistant for post-surgery care instructions—without having to start from scratch.
PlayAI’s PlayDialog is a model whose strength lies in its ability to adapt dynamically to multi-turn conversations, adjusting prosody, intonation, and emotional tone based on prior dialogue. This allows for more fluid, engaging, and contextually relevant interactions. Could this mean that, in the near future, a hospital can deploy a virtual care team of multiple AI agents conversing with a patient from different perspectives?
It’s worth noting that big tech companies (OpenAI, Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Nuance) also offer TTS services as part of their cloud platforms, and they, too, are improving steadily.
What does this mean for the future of healthcare?
AI-powered TTS is growing fast, with 20% annual adoption rates in healthcare. As technology improves, expect it to become a core part of patient care, making healthcare more efficient, inclusive, and human-centered. By handling routine tasks, personalizing patient interactions, and expanding access to care, AI voice technology isn’t just making healthcare faster—it’s making it better for everyone.
Better Communication, Better Care
Healthcare is all about clear communication, but brochures, rushed conversations, and language barriers can leave patients confused. AI voices solve this by making information more personal and accessible.
I’m thinking about a patient leaving the hospital with a complex medication schedule. Instead of a paper handout they might not understand, they get AI-powered voice instructions that remind them when to take each dose, explain side effects, and answer common questions. This approach has already boosted medication adherence by 45% and increased patient satisfaction by 60%.
AI voices also help break language barriers in telehealth. Instead of relying on a human interpreter, multilingual AI voice assistants allow doctors and patients to communicate fluidly in their own languages. Early studies show patients feel more comfortable and share more details when they can converse naturally rather than through a phone interpreter.
Cutting Costs Without Cutting Quality
Hospitals and clinics spend countless hours and dollars on repetitive tasks like appointment reminders, pre-op instructions, and follow-up calls. AI voices can handle these interactions instantly, freeing up staff for more complex care.
Here’s how the savings add up for a mid-sized hospital:
$180,000 saved annually by preventing avoidable readmissions.
$75,000 saved by reducing staff time spent repeating instructions.
$50,000 saved on interpreter services by automating multilingual communication.
$115,000+ saved by cutting down on paper materials and legal risks from miscommunication.
Beyond cost savings, AI voice assistants work 24/7, handling patient queries and even guiding them through basic medical concerns after hours. Instead of rushing to the ER over mild symptoms, patients can get AI-powered advice, preventing expensive and unnecessary visits.
Making Healthcare More Accessible for Everyone
AI voices are also breaking down barriers for non-English speakers, rural patients, and people with disabilities. Multilingual AI voices ensure that language isn’t a roadblock to understanding medical instructions. Patients with lower literacy levels can listen instead of reading complicated documents, making sure they get the right information.
In rural areas with limited doctors, AI-powered voice assistants help patients navigate symptoms, schedule follow-ups, and receive basic healthcare guidance—all through a simple phone call. Even low-tech feature phones can connect patients to these services, making healthcare accessible where it’s needed most.
For visually impaired patients, AI-powered screen readers with natural voices make medical information much easier to consume. For those with speech impairments, AI voices can even restore their ability to communicate by replicating their own voices.
…But we need to be careful with adoption
Challenges remain. Accuracy in healthcare is critical—mispronouncing a medication or dosage could have serious consequences. AI must also strike the right balance between efficiency and empathy. While a friendly AI voice can be helpful, it can’t replace the emotional connection of a human caregiver, especially in sensitive situations. Privacy is another concern, as voice-based healthcare systems must comply with strict regulations like HIPAA to protect patient data from breaches or misuse. Additionally, integrating AI into hospital workflows requires careful planning to ensure seamless collaboration between technology and human staff.
Despite these hurdles, AI voice technology has enormous potential to enhance healthcare, but we need to be careful with its implementation. We must ensure accuracy, maintain patient trust, and safeguard data while thoughtfully integrating AI into existing healthcare systems. The goal should be to augment, not replace, human care, making healthcare more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered.